If you suspect you were sold toxic backlinks or your website has lost ranking in Google due to spammy backlinks, your site received a manual action or lost trust during an algorithm update, please feel free to reach out to me for a backlink audit. I have taken care of toxic link issues on a wide variety of sites since Penguin rolled out in 2012, ranging from Los Angeles personal injury attorneys to international eCommerce organizations.
With that out of the way, let’s get on with identifying low quality links in case you want to take a shot at this yourself.
Were You Sold Low Quality Backlinks?
I’ve written this guide for business owners who have paid an SEO agency to help them rank higher in Google’s search results. That’s because everyone who has come to us for a link audit knew they needed backlinks but didn’t understand that the backlinks they were being provided could have a negative impact on their website’s visibility and performance in Google search. Unfortunately, at least 90% of SEO agencies out there get some really shady links.
I’ll admit, in some niches, linkbuilding is mandatory. For example, I work with personal injury attorneys. In any city in the world, each and every attorney on the front page is building links. However, better links come from “outreach”.
You were likely sold low quality backlinks if you paid for a certain number of links each month or the links were obtained rapidly. Quality linkbuilding takes a lot of time. In general, any purchased link is often a low quality backlink.
What are Low Quality Backlinks?
High quality backlinks have a positive impact on your site’s performance in search engines, such as Google. While this ranges from niche to niche, the highest quality link you can receive is generally from a reputable source, used in context, and in a topic relevant article.
A low quality backlink is easily identifiable by a search engine due to it’s obvious intent of algorithm manipulation. Some people call these “toxic links”. A toxic backlink will either provide no value to your site or have a negative impact. While it is necessary to seek out links in some competitive niches, you should always avoid low quality links. They will never help you and the only possible impact from low quality links is a negative impact.
A Brief History of Links:
Before we continue, you should understand how we got here.
When the hyperlink was invented, long before the web, it was specifically created so one document could cite a second document for further reading. It was basically for scientists. For example, in this article, I may want to cite this article about the invention of the hyperlink.
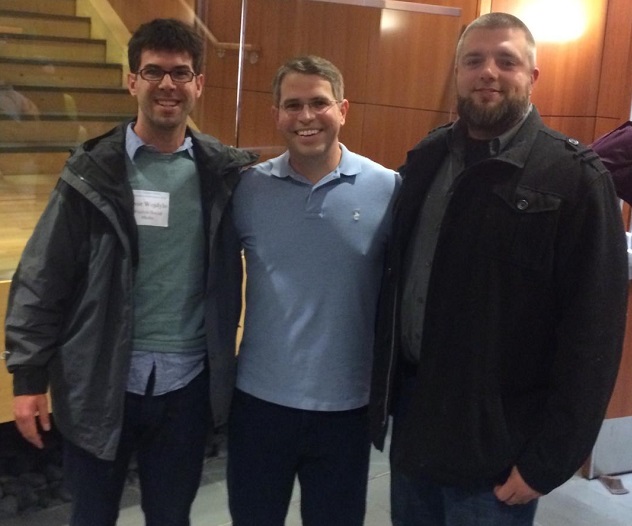
Early search engines ranked pages based on how many sites linked to them. That was about it. Of course, this was abused faster than you can spell SEO. Google’s engineers largely ignored this issue as they had bigger fish to fry such as making search safe, keeping adult content out of regular searches and legal problems. Eventually they had to change algorithms to reward quality over quantity. This was explained very well at a presentation by Google’s former head of webspam Matt Cutts. Great guy – I met him:
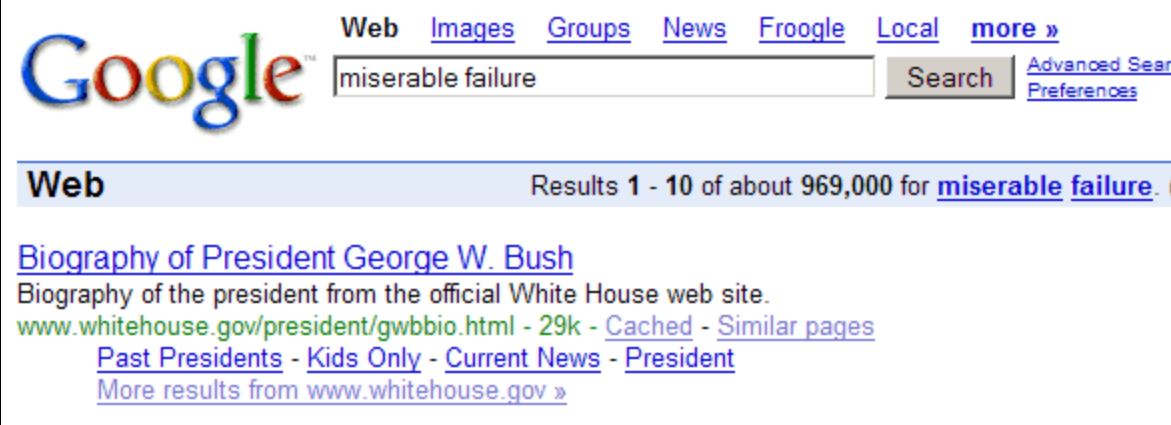
Next, “anchor text” (the text linked to another page) was the easiest way to spam Google. This came to a peak in 2007 when George Bush ranked for the term “miserable failure”. This forced Google to evolve again. Here’s a screenshot of the results of the most infamous “Google Bomb”:
In 2021 and beyond, Google is looking at the topical and geographical relevance of your links. If your want to rank in Fresno as a Fresno attorney, the best link you could get is from a high authority site in Fresno such as the Fresno Bee. For further reading, see my article on what natural anchor text really looks like.
Problems Caused by Low Quality Links:
There are many problems which can arise from having low quality links:
- Manual Action. A manual action is when a human reviewer at Google manually penalizes your website. When this occurs, your website is completely kicked out of the search engine.
- Algorithmic Penalty. In 2012, Penguin 1.0 rolled out, killing sites that were abusing anchor text links. Fast Forward to 2016, and Google made Penguin part of their main algorithm. Websites which have suffered an algorithmic penalty will receive a drastic, sudden drop in rankings and suffer a loss of traffic.
- Loss of Trust. There are many ways Google evaluates how much they trust a website, including the type of links you’re getting and how long you’ve been getting them for. This impacts rankings. Think about it, if you are an attorney, do you want referrals and mentions from the media, the Bar association, and other attorneys? Or do you want to be mentioned by a recipe website in Timbuktu?
- Nothing. Lucky for you, in many cases Google simply ignores low quality links. When Penguin 4.0 launched the search engine began devaluing links instead of demoting them. In a nutshell, this means they “usually” ignore low quality links instead of killing your rankings.
Identifying Low Quality Links:
Unfortunately, there are agencies in the SEO world who continue to intentionally misinform clients. However, identifying a bad / toxic / low quality links is simple and not up for debate. I’ve watched every tiny evolution of Google since day 1, and before them I watched Infoseek, Yahoo, Lycos and others. But you don’t have to take my word for it; every step Google has taken has been very well documented and is most definitely not a mystery.
Here are well known types of low quality links:
1. Links from spun content.
This is the most well known and glaringly obvious form of webspam. Obtaining links from spun content. Spun content is when someone takes an article and runs it through a piece of software which turns it into Jibberish. In the Google search rater guidelines this type of content is actually called the “lowest” quality content on the web. Google actively penalizes sites that do it. Even when this worked (10-15 years ago) I refrained from ever trying it as I have no intention on killing any of my own sites or client sites. This one is common sense.
As a note, Google considers a few types of content the lowest quality possible… “auto-generated content”, content which results in fraud, hate speech, scams, hacked sites, and pages which exist to deceive users. You do not want to associate yourself with anything Google considers low quality. To be honest, their standards aren’t even that high.
2. Anchor text stuffing.
Links pointing to your site for the exact phrases you’re trying to rank for are huge red flags.
Google clearly defines anchor text spam as “guest posting campaigns with keyword-rich anchor text links“.
In 2004, Google got this patent which clearly defined anchor text spamming: “Anchor text spamming involves obtaining a large number of web documents to link to a particular document using the same anchor text with which the document is to be associated.”
In 2007, Google made clear that they’re well aware of link manipulation which occurs in press releases and link building campaigns. They specifically state they pay special attention to “article marketing or guest posting campaigns with keyword-rich anchor text links.”
As you can see, this is an extremely old tactic which should never be used. Any search engine has been able to spot this for at least 14 years now. In general, any simple “tricks” will be worn out. If you use SEMrush you’ll even get warning alerts like this in your inbox if you happen to get an exact match anchor text link:
3. Blog comment spam.
I wish I didn’t have to mention this but apparently some people haven’t gotten the memo. Do not comment on other blogs just to get a backlink. Google ignores this type of user generated content and was penalizing sites for it long, long ago, since at least 2009.
4. Forum spam.
In 2020 I did a link audit for someone and they had fresh forum spam. This is unbelievable and one of the oldest tricks in the book. What happened was, software was created to make people accounts on forums, and in the user’s bio was a link to their website. Of course, this does not work, and it’s a gigantic red flag. In 2019, Google stated that they ignore Forum links. Over the years, plenty of people have been penalized who had forum spam links, but these days Google generally ignores UGC (User Generated Content).
5. Links from sites which abuse their outbound links.
If a site is linking out to casinos, locksmiths, or exists just to link out to other websites it should be avoided at all costs. The SEO community calls these “bad neighborhoods”. Low quality sites like this can be spotted by a search engine from 10,000 miles away. Do I really need to say more?
6. Link insertions on old content.
These links are sometimes called “niche edits” and usually cost between $5 and $20.
The way that it works is someone inserts a link to your site in an article that is a few years old.
Every website I’ve ever seen offering link insertions is part of a “PBN”, although niche edit spamming hacked websites is a new tactic being offered by the lowest of the low in SEO.
Rest assured, if someone is adding your links to old articles on the web, they most definitely do not have your best interests in mind. It doesn’t matter what you are paying, you have overpaid. If at all possible, it is best to get the work reversed. Keep in mind you are dealing with some extremely shady people.
7. PBN / Private Blog Networks.
A PBN, aka “Private Blog Network” is a batch of sites, maybe 100-500 sites, which exists to link out from each individual site to a destination site.
Unless you have spent many years carefully building your own PBN, any PBN you encounter in the wild is extremely dangerous as it leaves a huge, glowing footprint on the web which is very easily identifiable.
Google has been identifying these networks and crushing them for many years.
Your competitors can also simply tweet John Mueller (@JohnMu) or click this link to report a PBN.
8. Reciprocal link building.
This is another form of link building the Google killed many many years ago. It is sometimes called a “link exchange”. In 2020, I saw a law firm SEO agency still using the tactic. Unbelievable.
9. Paid links.
Technically, any paid link is spam. Can Google identify all of these? No. However, if your article is on a page which says “sponsored post”, it is very easy to tell that you paid to put it there. If it is easy for you to tell a link was paid for, it’s easy for Google to tell. If you’re going to pay webmasters to add content to their site, you have to be very very sneaky about it.
10. Low quality directories.
Last but not least, low quality directories are garbage. Using these is unlikely to hurt your site, but it is definitely not going to help it. In the world of attorney marketing, there are a handful of agencies who submit your site to 10 new directories each month so that they can check off your linkbuilding deliverable. This is a scam. There are hundreds, if not thousands of low quality directories on the web. If your links only come from directories, search engines will be forced to conclude that your website is worthless.
Recap:
This is not a one size fits all article. The way Google ranks a website about cancer is much different than the way they rank a website about finding an attorney. However, for most business owners, attorneys and bloggers reading this, they should now at least be aware of what a “bad backlink” is.
If you have bad links pointing at your site, you should have them assessed. Proactively removing them is always the best option. If you’re been penalized, you will likely need to disavow the bad links, which is a painful, slow process.
- Google “Pure Spam” Penalty Deindexes Sites March 6 2024 - March 12, 2024
- What Happened to ChicagoNow.com? - August 30, 2022
- The December 2021 Google Local Pack Algorithm Update - December 17, 2021




Leave a Reply